STEPS IN SEGMENTING, TARGETING, POSITIONING
Target Marketing
TARGET MARKETING
Identifying a set of possible competitive advantages to build a position
Choosing the right competitive advantages
Selecting an overall positioning strategy
Competitive advantage is the advantage over competitors gained by offering greater value either through lower prices or by providing more benefits that justify higher prices.
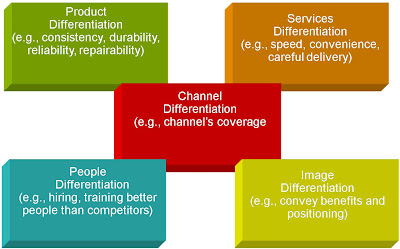
Possible Differentiation and Competitive Advantages
Overall positioning strategy (Value proposition)
Target Marketing
- Evaluating Market Segments
- Segment size and growth
- Segment structural attractiveness
- Level of competition
- Substitute products
- Power of buyers
- Powerful suppliers
- Company objectives and resources
Target Marketing: Selecting Target Market Segments
TARGET MARKETING
Target Marketing: Selecting Target Market Segments
Undifferentiated marketing - targets the whole market with one offer.
- Mass marketing
- Focuses on common needs rather than what’s different
- Goal is to achieve higher sales and stronger position
- More expensive than undifferentiated marketing
- Limited company resources
- Knowledge of the market
- More effective and efficient
- Local marketing
- Individual marketing
Identifying a set of possible competitive advantages to build a position
Choosing the right competitive advantages
Selecting an overall positioning strategy
Competitive advantage is the advantage over competitors gained by offering greater value either through lower prices or by providing more benefits that justify higher prices.
Possible Differentiation and Competitive Advantages